Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration involve chemical reactions which take place in the cell to produce energy which is needed for active processes.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form. In contrast to simple combustion cellular respiration involves the step-wise release of energy in a tightly regulated fashion. In this process glucose is broken down in the presence of molecular oxygen into six molecules of carbon dioxide and much of the energy released is preserved by turning ADP and free phosphate into ATP.
Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n. Where cellular respiration happens. Cellular respiration refers to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often synonymous with aerobic respiration.
Cellular respiration is the set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products. The principal carbohydrate formed through photosynthesis is glucose. Cellular respiration stores chemical energy in the form of phosphorylated nucleotides primarily ATP by means of oxidative reactions and makes it available to other reactions.
Glucose and then stored in energy-carrying biomolecule eg. Some organisms such as plants can trap the energy in sunlight through photosynthesis see Chapter 5 and store it in the chemical bonds of carbohydrate molecules. The cellular context In the diagram at left 1 represents the cell exterior.
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products. Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration. The respiration occurring at the cellular level wherein the cells produce energy by combining oxygen with food molecules is called cellular respiration.
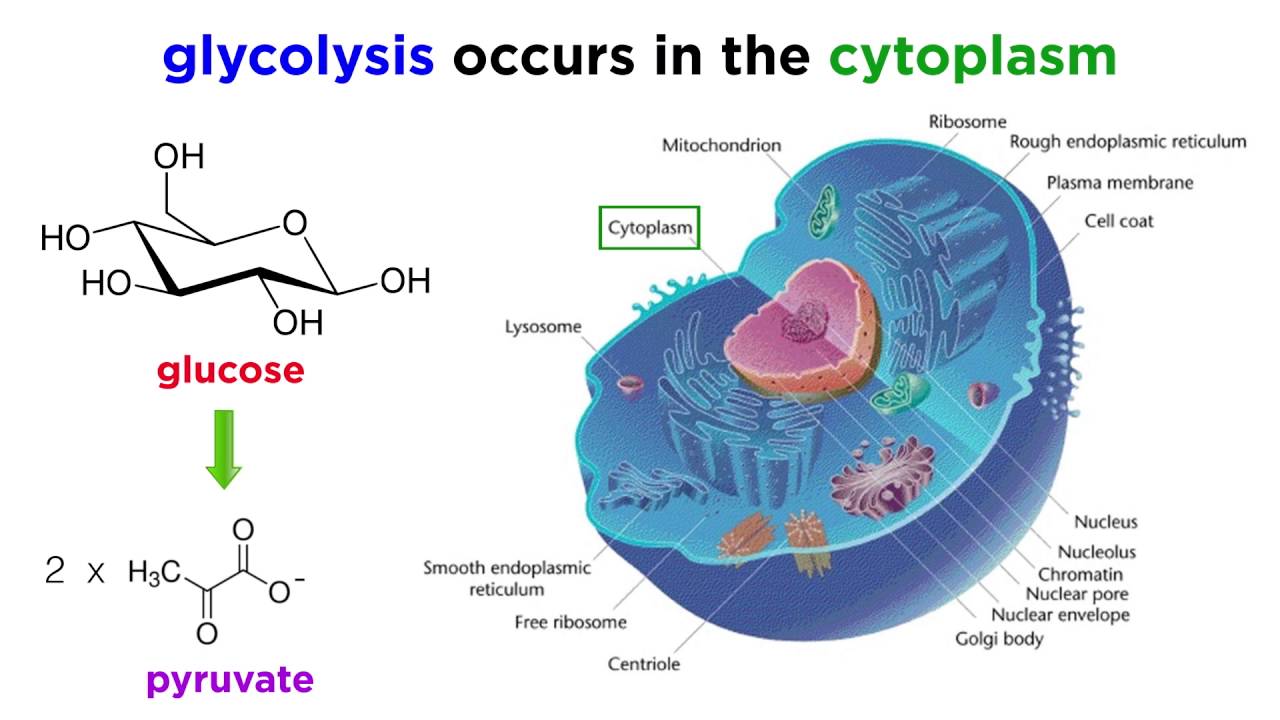
Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell. Anaerobic respiration is another type of cellular respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen and produces energy.