Marine Animals Definition Biology

The study of marine life is called marine biology and a person that studies marine life is called a marine biologist.
Marine animals definition biology. Earth is often referred to as the blue planet because seas and oceans cover more than 75 of the Earths surface. It is the largest and most diverse biome in the world. Most marine biologists choose a specialty field such as phycology ichthyology invertebrate zoology marine mammalogy fishery biology marine biotechnology marine microbiology or marine ecology.
In this context the word marine is interchangeable with saltwater. A marine biologist is someone who is interested in learning and studying marine organisms and what their lives are like in their natural habitats. Spongocoel- spacious cavity in sponge.
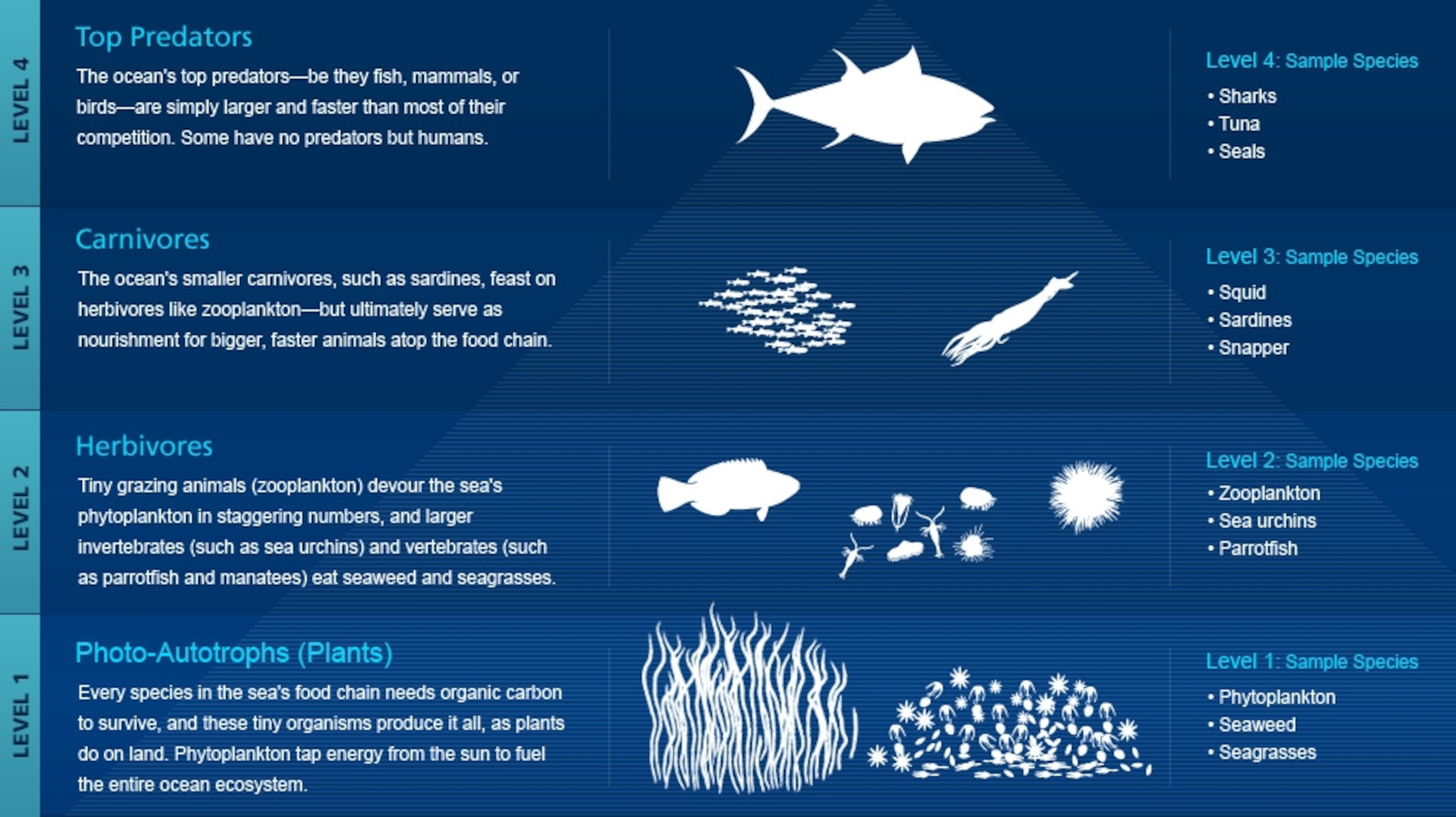
Marine biology is the study of marine ecosystems marine organisms and human interactions with these environments and species. The scientific study of organisms living in or dependent on the oceans. Not only that but water provides a 3-dimensional habitat which increases the available habitat for the animals microbes and plants to live.
When many people think about a marine biologist they picture a dolphin trainer. Archaeocytes- cells that move through the sponge. Marine environments are therefore the most common habitat on Earth.
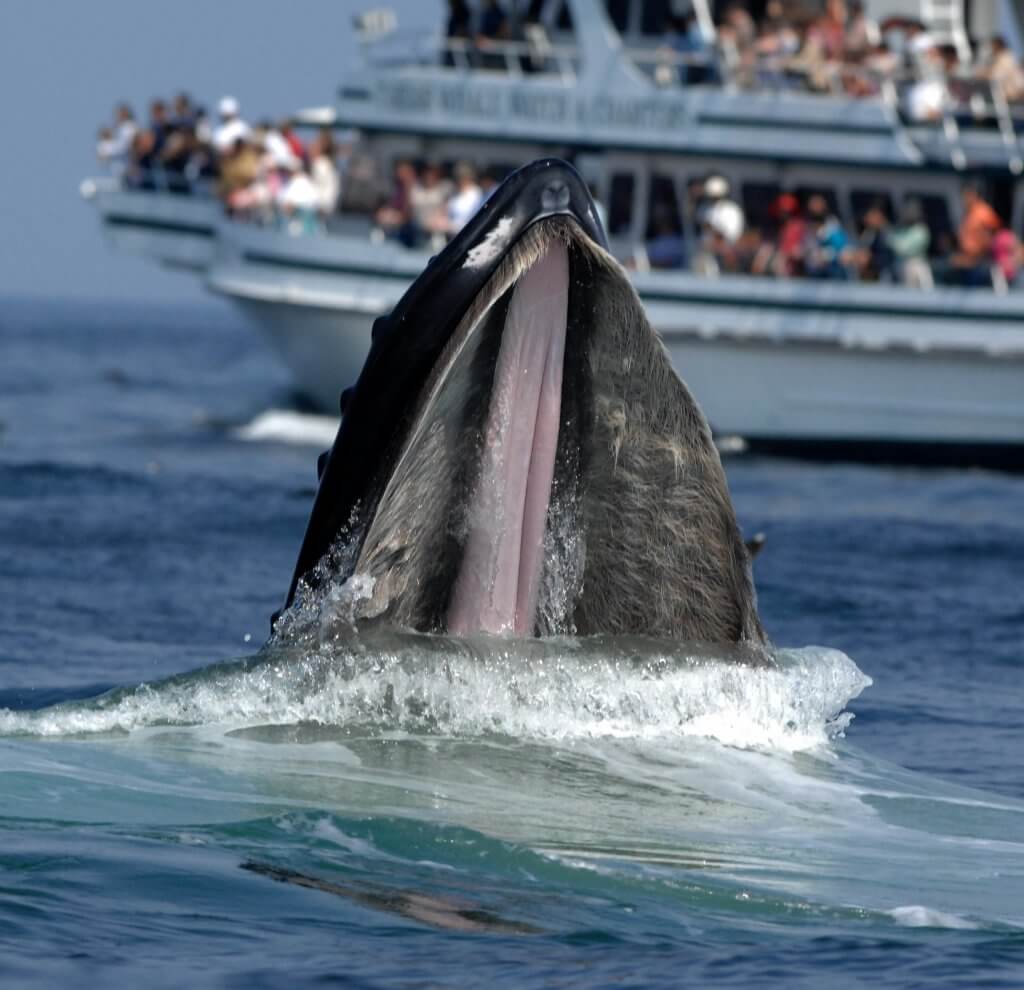
Spongin- flexible protein fibers. These organisms take many forms from the tiniest single-celled plankton to the largest animal on Earth the blue whale. Marine biology is the scientific study of plants and animals that live in salt water.
But marine biology is so much more than making a dolphin -- or sea lion -- follow commands. Look it up now. Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life organisms in the sea.